Good practices to protect yourself from this fraud.
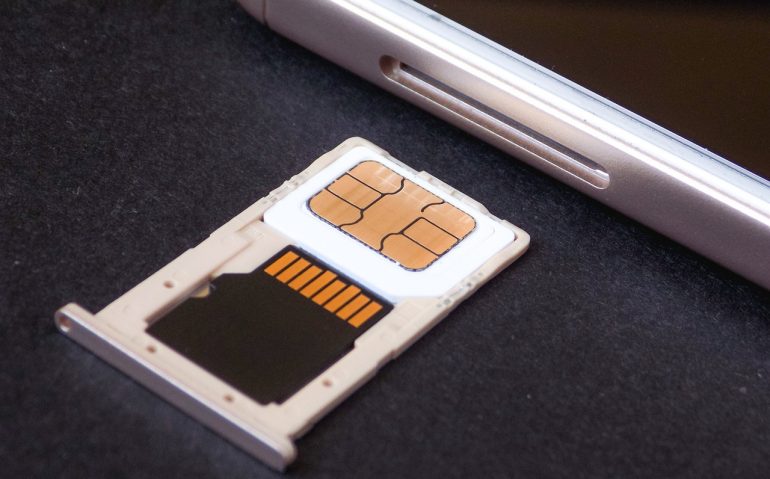
‘SIM swapping’ is a scam that consists of fraudulently duplicating the SIM card of a person’s mobile phone. First, the cybercriminal impersonates him to obtain the duplicate. Then, once the victim loses phone service, she accesses their personal information and takes control of their digital banking using verification SMS that arrives at the phone number.
Cybercriminals usually contact the telephone operator through a call or in person and provide the victim’s personal and private information, such as her ID number, to impersonate her. This data may have been previously collected by carrying out other social engineering attacks on those affected (fraud through SMS, email or phone call in which they impersonate trusted companies or entities to try to deceive them) or by investigating their social networks.
Victims’ sensitive data can also be obtained if they have downloaded fraudulent applications on their devices, designed by cybercriminals to steal this type of information, or if they have connected to fake Wi-Fi networks created to achieve this goal.
The main risk of a duplicate SIM card is that when it is done through a phone call, physical identity verification is not carried out. The company operator requests certain personal and banking data; If the scammer has obtained this information through any of the attack methods mentioned above, she could acquire the duplicate.
There are a number of good security practices that reduce the chances of suffering a SIM swapping attack and help protect information if it occurs:
-
- If it is detected that the phone has been left without coverage for no logical reason, contact the telephone operator to notify it and check what has happened. In case the duplicate card is confirmed, it is necessary to immediately change the access credentials to digital banking and other frequently used online services and contact the bank to report what happened.
- Never provide personal or banking information through links included in suspicious emails or SMS or in unsolicited calls.
- Properly configure the privacy and security settings of your social network profiles, so that only your contacts can see the information that is published on them. In addition, these platforms must be protected with strong passwords and it is not recommended to share private information that could be used by third parties for malicious purposes.
- Download applications from official markets, such as Google Play or App Store, and grant them only the permissions necessary for their correct functioning.
- Do not enter sensitive information, such as passwords and banking details, if the device is connected to a public Wi-Fi network.
- When faced with charges of unknown bank transactions, it is necessary to contact the bank as soon as possible to explain what happened.
- Save all the evidence you have available to file a complaint with the Security Forces and Corps in case you are a victim of this scam.